At AQUILA, our clients often ask our industrial team how to find the right industrial space for their company. Industrial buildings may appear similar but there are unique aspects and different uses for each type of industrial space.
In this article, you will find overviews and uses of the following:
- Bulk distribution warehouses
- Manufacturing buildings
- Cold storage buildings
- Data centers
- Flex buildings
Read Next: How Much Does It Cost to Lease Industrial Space in Austin, Texas? (Rental Rates)
Types of Warehouse Buildings
Warehouses are generally large, one-story buildings with high ceilings (18 to 32 ft clear) and multiple dock-high (48 inches) loading doors on either the front or back of the building to accommodate the loading and unloading of larger trucks.

Dock high-loading doors at Getagadget warehouse space.
Warehouse buildings are usually used for storage and distribution, which means only a small amount of office space is needed and most of the space will be dedicated to storing products and inventory.
Warehouses also usually have large concrete truck courts to accommodate frequent traffic from 18-wheelers and large box trucks.
Some warehouse users may also have specific HVAC requirements. Most distribution warehouse spaces are not air-conditioned. However, more and more tenants are adding air conditioning to their warehouse spaces in order to attract employees in the Texas heat. It’s important for prospective tenants to understand the condition of the HVAC system in a space when considering warehouse options.
Read Now: How Much Does It Cost to Lease Industrial Space in Austin, Texas? (Rental Rates)
Bulk Distribution Warehouses
Bulk distribution warehouses are ideal for tenants such as logistics and distribution companies who need to ship goods to businesses or consumers.
These buildings typically have 5% to 10% of the overall square footage dedicated to office area with the rest dedicated to warehouse space. They also have lower parking ratios than other types of industrial buildings, because there are usually fewer employees working in these spaces and little (or no) customer traffic.
Location is a key factor for logistics and distribution companies when choosing a building because most of their business is done through truck transportation. Because of this, these buildings are usually located on or near major interstates and thoroughfares in order to make it easily accessible for 18-wheelers and allow for direct connection to other major cities. Depending on how tenants receive and distribute their goods, it can also be important to be located near an airport.
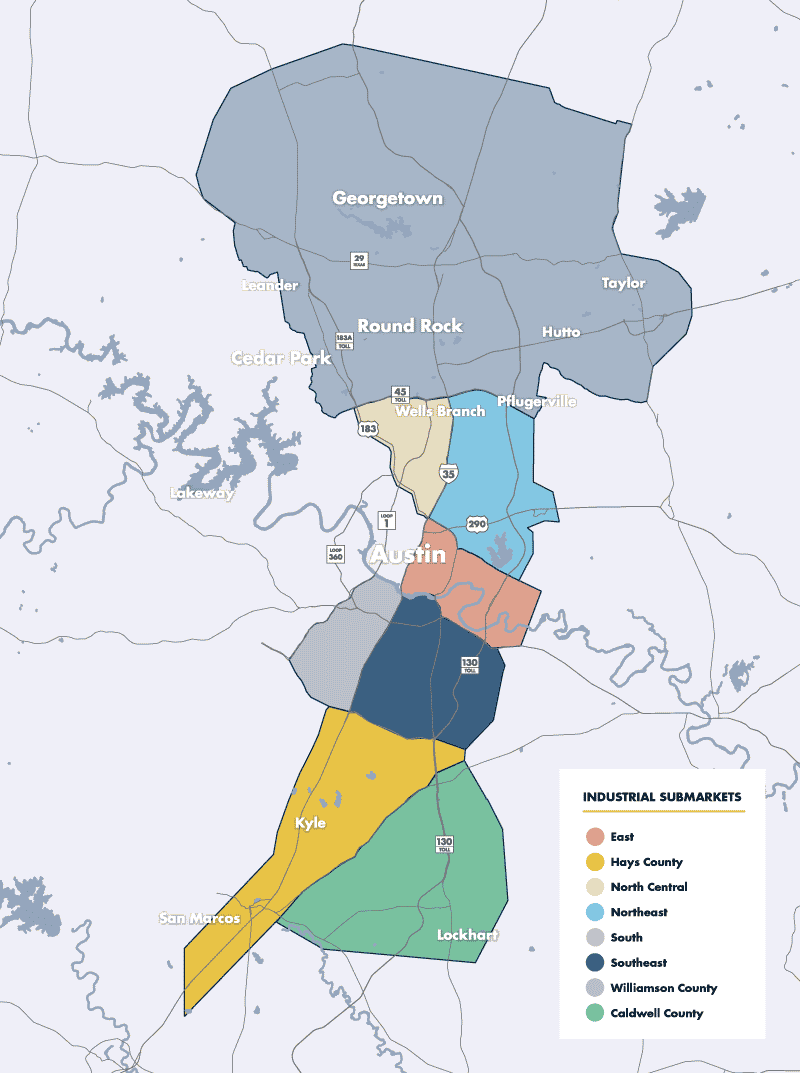
In Austin, the majority of bulk distribution buildings are located in three main industrial submarkets:
- Southeast Austin, which provides proximity to Austin-Bergstrom International Airport and easy access to South Austin, San Antonio, Houston, Dallas, and the Rio Grande Valley via Hwy 71, US-183 and IH-35.
- Northeast Austin, near the intersection of IH-35, US-183, and US-290 East. Its relatively central location and access to major roadways make this a great area for logistical and distribution companies. It also allows them to reach all parts of the Austin metro area as well as Williamson County, Houston, Dallas, and San Antonio.
- North Central Austin, which encompasses Mopac/Loop 1, IH-35, and US-183. This is an older established industrial area that is in a good location for businesses and distributors serving customers in North Austin and Williamson County. The flex buildings in this area have recently become popular with tech tenants who are looking for value office space near the Domain and other retail and restaurant hubs in the area.
The optimal location for a warehouse tenant depends largely on how that company receives its inventory and where the customer base for those products is located.
Specialized Warehouses
Some warehouse buildings are used by tenants with specialized needs such as manufacturing, cold storage, and data centers.
Manufacturing Buildings
Unlike most bulk distribution warehouses, manufacturing buildings often have highly specialized infrastructure and finishes, including heavy electrical power. Depending on a company’s needs they may also have user-specific drainage, ductwork, ventilation systems, oversized loading docks, and water, gas, or chemical lines.
Manufacturing buildings often house companies that are producing products using special machinery, chemicals, or materials.
Individual manufacturing buildings are less prevalent in Austin because the city has historically not had a large manufacturing presence compared to San Antonio or Houston. Oftentimes, smaller manufacturing companies will use distribution warehouse space for their manufacturing needs. However, retrofitting a warehouse space for manufacturing use can be cost-prohibitive if it requires a significant power upgrade or other major modifications to a space. Because of the specialized nature of their individual businesses, manufacturing companies will often need to have these types of buildings custom-built.
Semiconductor manufacturers, breweries, food producers, and machinery manufacturers are some of the types of businesses needing manufacturing space in Austin.
Read Next: Who Are the Best Industrial Brokerage Firms in Austin Texas?
Cold Storage Buildings
Another highly specialized use for warehouse buildings is cold storage. Because of the high cost to build out, cold storage space for individual tenants is limited in Austin. Most cold storage facilities in this area are single-user buildings built specifically for large national food distribution and manufacturing companies.
Cold storage warehouses have large-capacity coolers and freezers to store food or other temperature-sensitive items. This type of storage may also require a specialized foundation because the freezing, often sub-zero, temperatures in the coolers can cause slabs to crack.
Because of the types of products arriving and being distributed, these buildings also require seals on their docks and insulated overhead doors to keep the products cold.
Data Centers
Datacenter tenants are another specialized user for warehouse buildings. Data centers typically house rows and rows of computer servers, massive amounts of cabling, and telecommunications equipment and have very few employees.
To support this data storage, these buildings require large amounts of electricity from reliable and consistent power sources. These buildings almost always include backup generators as well as extensive security systems. Data centers are found in areas with at least two power stations nearby. These “redundant power” sources help ensure that in the event of a power failure or system issues, the data storage will not be affected and ensures zero downtime. Data center users also typically require at least two fiber providers to their space to ensure the flow of information should a single fiber provider lose connectivity.
Depending on the tenant, the flooring sometimes has to be customized and raised for cabling and cooling for the equipment. These types of buildings also require robust supplemental HVAC systems to keep the servers and other equipment cool.
Types of Flex Buildings
Flex buildings are, by design, “flexible” and allow for a wide range of office and warehouse uses. They can be used for many purposes and are easier to retrofit to meet a company’s needs than typical warehouse buildings. This flexibility is ideal for a wide range of companies that need office space with a warehouse component. Flex buildings usually have slightly-lower ceiling clear height (14 – 24 ft clear) and have a larger percentage of office space than a typical distribution warehouse building. They also have more parking and nicer landscaping than other industrial buildings.

Pictured: Tech Center Southwest flex office space.
Most flex buildings have some type of overhead loading doors, but tenants should be sure the loading situation works for their use. The loading areas in flex buildings can be dock high, or grade-level (ground-level), and older buildings may even have semi docks (2 ft) that can accommodate smaller box trucks and vans.
Flex space can work well for value office tenants like startups because the rates are typically much lower compared to traditional office space and can accommodate more parking than bulk warehouse buildings.
Research and Development Uses
Flex buildings are often preferred by companies doing research and development in the technology and biotechnology industries.
Research and development spaces are usually a mix of office, testing areas, and smaller warehouse spaces, depending on the needs of the tenant. They usually require slightly more power than typical flex space for testing equipment and can sometimes be highly specialized.
For example, a 40,000-square-foot electronics tenant may have a 10,000-square-foot office space for their executive, administrative and sales teams at the front of the building, with 20,000 square feet of warehouse for product manufacturing and storage, and 10,000-square-foot of space set up as an electrical testing lab.
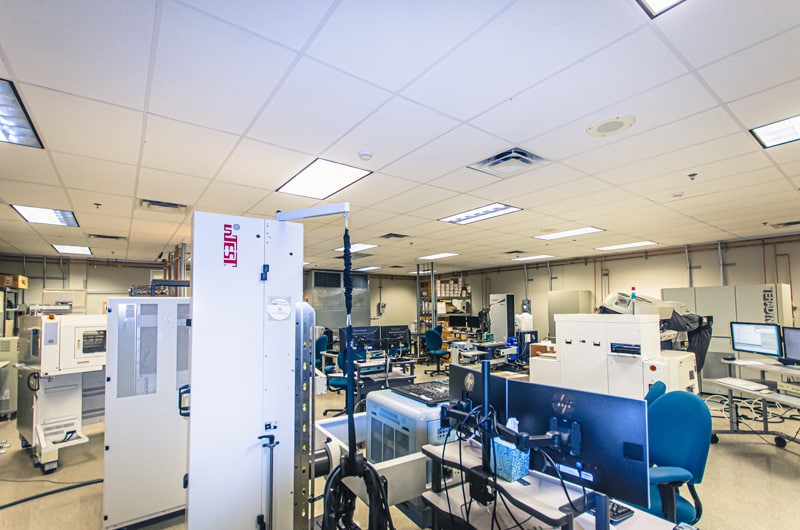

Southpark Commerce Center 2: an industrial building with lab bays, heavy power, IT infrastructure, and a generator included.
Conclusion
While most industrial buildings, from distribution to flex, may have their similarities, it’s important to note the differences to find the best space for you. To get the best idea of what space fits you, schedule a consultation with one of our industrial brokerage specialists today.













